Featured topic
Intelligent Agreement Management
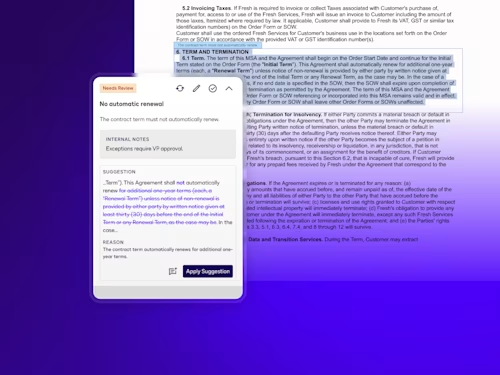
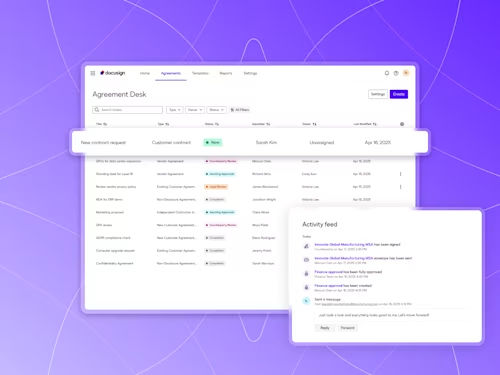
See how Intelligent Agreement Management helps organizations to create, commit to, and manage agreements through a single, streamlined workflow.
Popular posts
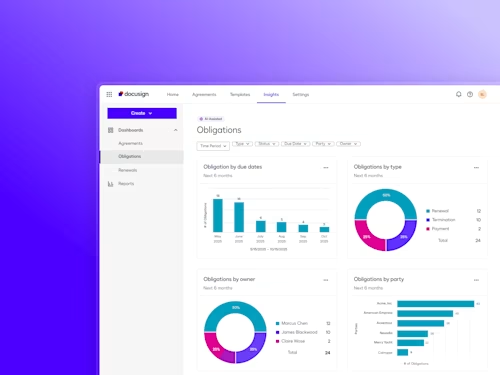
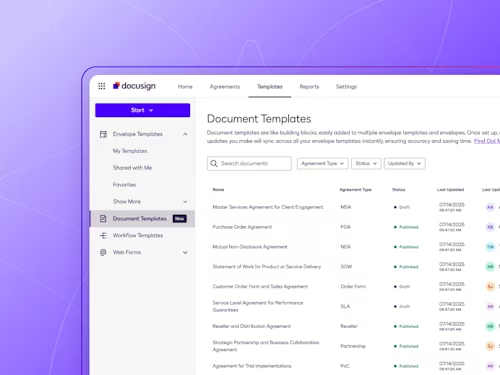
Digitize and Organize Your Agreements in a Central Repository
With Docusign IAM, all existing eSignature agreements are automatically stored in Navigator.

Agreement strategies and insights - delivered right to your inbox
Docusign IAM is the agreement platform your business needs