Eliminate repetitive agreement tasks to streamline workflows and reduce turnaround time
Build an extension app that imports agreements from your cloud storage system into the AI-assisted Docusign Navigator to easily find, report on, and manage agreements.
Across industries, engineering teams are working to eliminate a common drag on efficiency: large volumes of agreements that are difficult to find and manage. Until a solution is implemented, employees spend countless hours searching across locations, opening files one by one, and skimming them to find information needed for payments, renewals, terminations, and other obligations.
If your task is to free users from time-consuming, repetitive agreement work, Docusign for Developers provides tools you can leverage for a custom solution that consists of the following:
Implement an application that uses the file input from cloud storage feature to automate importing your organization's agreements into the Docusign Navigator repository.
After import, Navigator AI analyzes the files, classifies them, and extracts key data.
Your organization can then use Navigator to easily find and report on agreements and manage obligations. This results in streamlined workflows with shorter turnaround times.
This blog post focuses on the first component of this process—implementing an extension app to import files from your cloud storage system into Navigator. Docusign supports import from commonly used cloud storage systems, as well as proprietary platforms.
If this isn't the solution you're looking for, you may find it in one of these other blog posts:
Reducing manual agreement work: Automating file export to cloud storage: Archive completed agreements from the Docusign platform to your cloud storage system to comply with auditing, retention, and other requirements.
From NIGO to STP: A developer's guide to custom data verification and the Connected Fields API: Generate agreements, verify their values against your system of record, and enable users to correct data before submittal.
Our use cases are another great resource for learning how Docusign can solve specific issues that your organization faces.
What is an extension app?
At the core of the solution described here is an extension app. This is an application that provides additional functionality for Docusign agreement processes by receiving API requests from Docusign and executing the business logic associated with the requests. Depending on the features required, an extension app works with one or more of the supported extensions. Each extension has a set of requests that Docusign sends to the extension app to implement the extension's features.
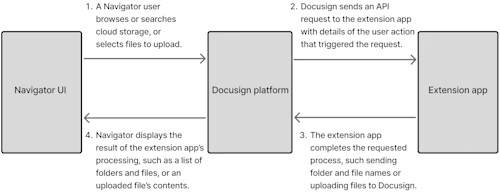
For this use case, the file input cloud storage extension is used. This extension's requests are triggered when a Navigator user browses cloud storage drives or folders, searches for files or folders, and uploads files. The request flow is shown below.
How does an extension app streamline file import?
Before we get into the technical details of building a solution, let's take a look at how your users will be able to easily import files into Navigator after you've implemented a file input from cloud storage extension app.
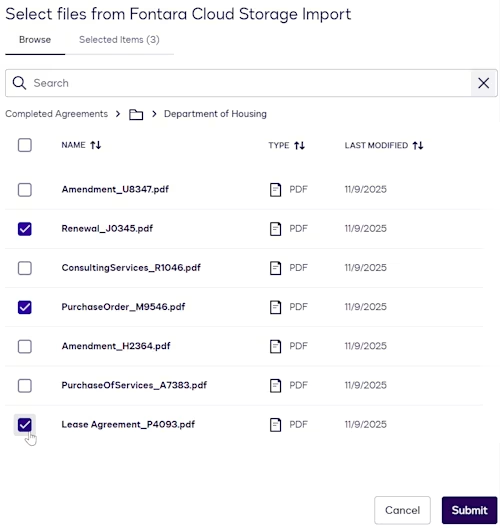
The user selects cloud storage files for import
A Navigator user can locate files on the cloud storage system by browsing directories or searching by name. After locating and selecting files, a user initiates the upload.
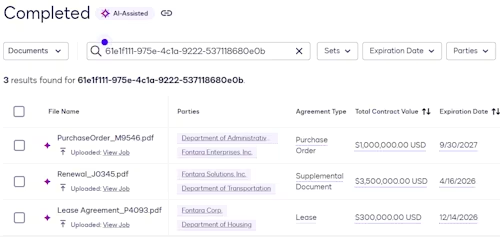
The user reviews the import results
When the upload is complete, the user can view a list of imported files in the Agreement List Table, which displays the file name and some of the AI-extracted values.
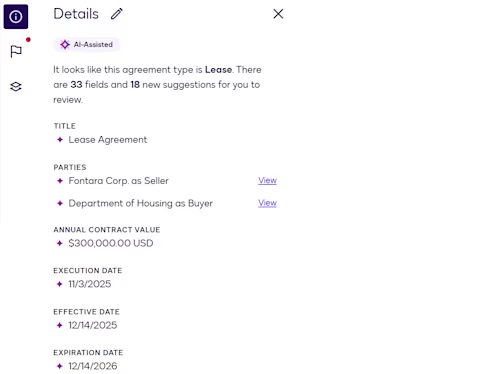
The user reviews and updates AI-extracted data
The user can review the AI-extracted agreement data for each file on the Agreement Preview Page and update the data points as needed.
The Navigator user documentation explains how users can manage agreements that have been uploaded into Navigator. It covers topics such as search capabilities, obligation management, and dashboards and reports.
The next sections explain how to implement a file input from cloud storage extension app that can be tailored to your organization’s business needs. You can also review the implementation process in this video:
What's the process to implement an extension app?
Extension app implementation consists of four main phases:
Build the app: Create an API service that Docusign can call and any backend processing associated with the API requests.
Register the app: Provide Docusign with the information it needs to send requests to your app.
Test the app: Use Docusign tools and procedures to verify the extension app functionality.
Publish the app: Initiate a review with Docusign to make the app available for production use.
See the next sections for details.
Build an extension app
Your organization creates an extension app that can receive and respond to requests that Docusign sends to your app’s API endpoints. These requests are described in the next sections. Details about the request and response formats appear in the file input cloud storage extension contract reference.
List Drives request
Docusign sends this request when a Navigator user starts the process of locating files for upload. The request obtains a list of drives on the cloud storage system. If the cloud storage system organizes folders and files under a different container type, the request can retrieve those containers instead.
This request is optional. If it is implemented, a user can select the drive or other container type in which to browse for files. If this request is not implemented, the extension app’s business logic must select the drive or other container type.
An example List Drives response is shown here:
{
"containerType": "drive",
"data": [
{
"containerId": "47",
"containerName": "Requests for Proposals"
},
{
"containerId": "48",
"containerName": "Bids"
},
{
"containerId": "49",
"containerName": "Completed Agreements"
}
]
}List Directory Contents request
Docusign sends this request when a user selects a cloud storage drive or directory on the Navigator Select Files window. It obtains a list of folders and files in the selected drive or directory.
An example List Directory Contents response is shown here:
{
"parentId": "488",
"data": [
{
"type": "file",
"name": "Lease Agreement_P4093.pdf",
"id": "4891",
"mimeType": "application/pdf",
"parentId": "488",
"lastModifiedDate": "2025-11-09T20:32:51.566Z"
},
{
"type": "file",
"name": "Renewal_J0345.pdf",
"id": "4782",
"mimeType": "application/pdf",
"parentId": "488",
"lastModifiedDate": "2025-11-09T20:32:51.566Z"
},
{
"type": "file",
"name": "PurchaseOrder_M9546.pdf",
"id": "4792",
"mimeType": "application/pdf",
"parentId": "488",
"lastModifiedDate": "2025-11-09T20:32:51.566Z"
},
{
"type": "folder",
"name": "Terminated Contracts",
"id": "501",
"parentId": "488"
}
]
}Search request
Docusign sends this request when a user enters a search string on the Navigator Select Files window. It obtains a list of matching cloud storage folders and files.
An example Search response is shown here:
{
"results": [
{
"type": "file",
"name": "Lease Agreement_P4093.pdf",
"id": "4891",
"mimeType": "application/pdf",
"parentId": "488",
"lastModifiedDate": "2025-11-09T20:43:57.060Z"
}
]
}Get File request to the external service
Docusign sends a Get File request when a Navigator user initiates a file upload. The request includes the file ID that the external service returned in response to a List Directory Contents or Search request.
The request also includes an x-docusign-session header that the external service must parse to obtain several values. The service uses these values in subsequent requests that it sends to Docusign to upload the file and report the upload results. The values are:
sessionToken: A token that is unique to the Get File request and contains encoded claims.expiresAt: The date and time at which thesessionTokenexpires, in ISO 8601 UTC format.filesApiUrl: The Docusign URL to which the external system should send the file upload request.callbackUrl: The Docusign URL to which the external system should send the callback request to report the upload results.
Upload request to Docusign
After responding with a 202 Accepted status to the initial Get File request, the external service sends an upload request to Docusign that supplies the contents of the requested file as a stream of raw bytes. The request is sent to the filesApiUrl that the service extracted from the Get File request's x-docusign-session header. The request's Authorization header must contain the sessionToken from the x-docusign-session header.
Callback request to Docusign
After receiving a response to the upload request, the external service sends a callback request to Docusign to indicate whether the upload succeeded. The request is sent to the callbackUrl that the service extracted from the Get File request's x-docusign-session header. The request's Authorization header must contain the sessionToken from the x-docusign-session header. The callback request body includes an upload status and identifies the uploaded file using an ID returned by Docusign in its response to the upload request.
The sample code below shows a TypeScript function that uses the parsed values from the x-docusign-session header to send an upload request and a callback request to Docusign.
async function sendUploadRequestWithSessionToken(uploadUrl: string, callbackUrl: string, sessionToken: string, filePath: string): Promise<FileImportResponse> {
try {
const buffer = fs.readFileSync(filePath);
const uploadResponse = await fetch(uploadUrl, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Authorization': `Bearer ${sessionToken}`
},
body: buffer
});
const uploadResponseData = await uploadResponse.json();
const uploadDocumentId = uploadResponseData.id;
var callbackData;
if(uploadResponse.ok) {
callbackData = { status: "EXECUTION_STATUS_SUCCEEDED", output: {data: {documentId: uploadDocumentId}} };
} else {
callbackData = { status: "EXECUTION_STATUS_FAILED", output: {data: {documentId: uploadDocumentId}} };
}
const callbackResponse = await fetch(callbackUrl, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': `Bearer ${sessionToken}`
},
body: JSON.stringify(callbackData)
});
if (!callbackResponse.ok) {
const errorData = await callbackResponse.json();
throw new Error(`HTTP error! Status: ${callbackResponse.status}, Message: ${errorData.message}`);
}
const responseData = await callbackResponse.json();
return responseData;
}
catch (error) {
console.error('Error sending POST request:', error);
throw error;
}
}See the file input from cloud storage reference implementation for sample code for all the extension's actions.
IT infrastructure to support the extension app
The infrastructure to support an extension app includes these components:
API proxy: Required if requests from Docusign are not in the format required by the extension app’s API endpoints, or if the responses are not in the format that Docusign expects.
Authorization: The extension app must support the authorization parameters that Docusign sends and meet the authorization response requirements.
Network configuration: Review the network setup required to ensure that Docusign can communicate with the extension app.
Register the extension app with Docusign
An extension app must be registered with Docusign. Registration provides Docusign with information it needs to obtain authorization from the extension app and send requests to its endpoints.
In addition, registration sets the extension app’s distribution options. See Globalization for information about setting the regions in which an app will be available. See Choosing private distribution instead of public for details about how to make an app available only to specified Docusign accounts or to all accounts.
Note: Only members of the Docusign Partner Program can publish a public extension app.
Extension apps can be registered in the Developer Console using a guided, form-based UI or by uploading a JSON extension app manifest file. Below is a sample app manifest file for an extension app that implements file input from cloud storage. Authorization parameters, including endpoint URLs, appear in the connections object. The extensions object specifies that this is a file input cloud storage extension. The actions object defines each request type that Docusign will send to the external service, including the endpoint URL. See App manifest reference for details about the file structure and properties.
{
"name": "Fontara Cloud Storage Import",
"description": {
"short": "Uploads a completed agreement from cloud storage",
"long": "Import files into the Navigator smart repository for AI-powered analysis."
},
"termsOfServiceUrl": "https://www.fontara.com/tos",
"privacyUrl": "https://www.fontara.com/privacy-security",
"supportUrl": "https://www.fontara.com/support",
"publisher": {
"name": "Fontara",
"email": "support@fontara.com"
},
"connections": [
{
"name": "authentication",
"description": "Secure connection to the extension app",
"type": "oauth2",
"params": {
"provider": "CUSTOM",
"clientId": "8d606a57-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-219e80c7ed16",
"clientSecret": "lfvZIU...GCreU=",
"scopes": [],
"grantType": "authorization_code",
"customConfig": {
"authorizationMethod": "header",
"authorizationParams": {
"prompt": "consent",
"access_type": "offline"
},
"authorizationUrl": "https://fontara.com/api/oauth/authorize",
"requiredScopes": [],
"scopeSeparator": " ",
"tokenUrl": "https://fontara.com/api/oauth/token",
"refreshScopes": []
}
}
}
],
"screenshots": [],
"extensions": [
{
"name": "File Input Cloud Storage Extension",
"description": "Imports files from cloud storage",
"template": "FileIO.Version1.FileInputCloudStorage",
"actionReferences": [
"list-directory-contents",
"list-drives",
"get-file",
"search"
],
"capabilities": [
"FileIO.Version1.ListDrives"
]
}
],
"actions": [
{
"name": "list-directory-contents",
"description": "Lists directory contents",
"template": "FileIO.Version1.ListDirectoryContents",
"connectionsReference": "authentication",
"params": {
"uri": "https://fontara.com/api/listdirectorycontents"
}
},
{
"name": "list-drives",
"description": "List drives",
"template": "FileIO.Version1.ListDrives",
"connectionsReference": "authentication",
"params": {
"uri": "https://fontara.com/api/listdrives"
}
},
{
"name": "get-file",
"description": "Imports a file",
"template": "FileIO.Version1.GetFile",
"connectionsReference": "authentication",
"contractType": "action-with-callback",
"params": {
"uri": "https://fontara.com/api/getfile"
}
},
{
"name": "search",
"description": "Searches files and folders",
"template": "FileIO.Version1.Search",
"connectionsReference": "authentication",
"params": {
"uri": "https://fontara.com/api/search"
}
}
],
"signupUrl": "https://www.fontara.com/signup",
"publicationRegions": [
"US"
],
"distribution": "PRIVATE",
"icon": {
"data": "iVBORw…Jggg==",
"mediaType": "image/png"
}
}Test the extension app
After an extension app has been registered with Docusign, these Developer Console testing features verify that Docusign can access the extension app:
Connection test: Verifies that Docusign can obtain authorization from the extension app
Extension tests: Verify that Docusign can send requests to the extension app or API proxy endpoints and process the responses. The Get File extension test sends an
x-docusign-sessionheader with the request to the external service.
For help with common errors such as authorization or API request failures, see the extension app Troubleshooting page.
Docusign also recommends performing a test from the Navigator UI to confirm that the extension app is invoked from Navigator, retrieves file and folder information, and uploads the selected files successfully. See File input cloud storage extension Navigator test for details.
Publish the extension app
To use a file input from cloud storage solution in production, you must submit the app for Docusign review. After Docusign approves it, you can publish it for use in the production environment. If you registered the extension app for public distribution, it will be available on the App Center for any Docusign user to install and use. If you registered the app for private distribution, it will be accessible only to your organization or your customers.
Conclusion
Agreement management is frequently characterized by time-consuming searches across storage locations and manual intervention to manage obligations. Importing files into Navigator for AI-assisted data extraction can save time and ensure that obligations are addressed reliably. You can create a secure, easy-to-use file import process by following the steps outlined here to:
Build an extension app
Register the extension app
Test the extension app
Publish the extension app
Your users can then leverage Navigator's capabilities to manage agreements more efficiently.
The Docusign for Developers suite of tools provides everything you need to develop an application tailored to your organization’s or your customers’ specific business cases. To take the first steps, visit the Docusign Developer Center to sign up for a free developer account and learn more, or explore the benefits of the Docusign Partner Program. Ready to try it? Get started with our file input from cloud storage reference implementation.
Additional resources
Read an introduction to the file input cloud storage extension.
Get details about the extension’s requests and responses.
Learn what you can do with Navigator.

Julie Gordon joined Docusign in 2021. As a member of the Developer Content and Advocacy team, she creates content, media, and code to help developers learn how to use Docusign technology. With a background in software quality assurance and technical writing, she produces meticulously researched and tested documentation of APIs, developer tools, and low-code/no-code platforms.
Related posts
Docusign IAM is the agreement platform your business needs



