Platform safety
A Multi-Layered Defense. Docusign's anti-fraud strength comes from layers of security that work together to protect documents, verify identities, and control processes.
Ensuring document integrity
This section explores the features that guarantee a document has not been tampered with and that provide a complete, court-admissible history of every action taken. These form the foundational evidence of a transaction's validity. This ensures a comprehensive audit trail. Every action is tracked, from creation to completion.
This detailed log provides undeniable proof of the signing process.
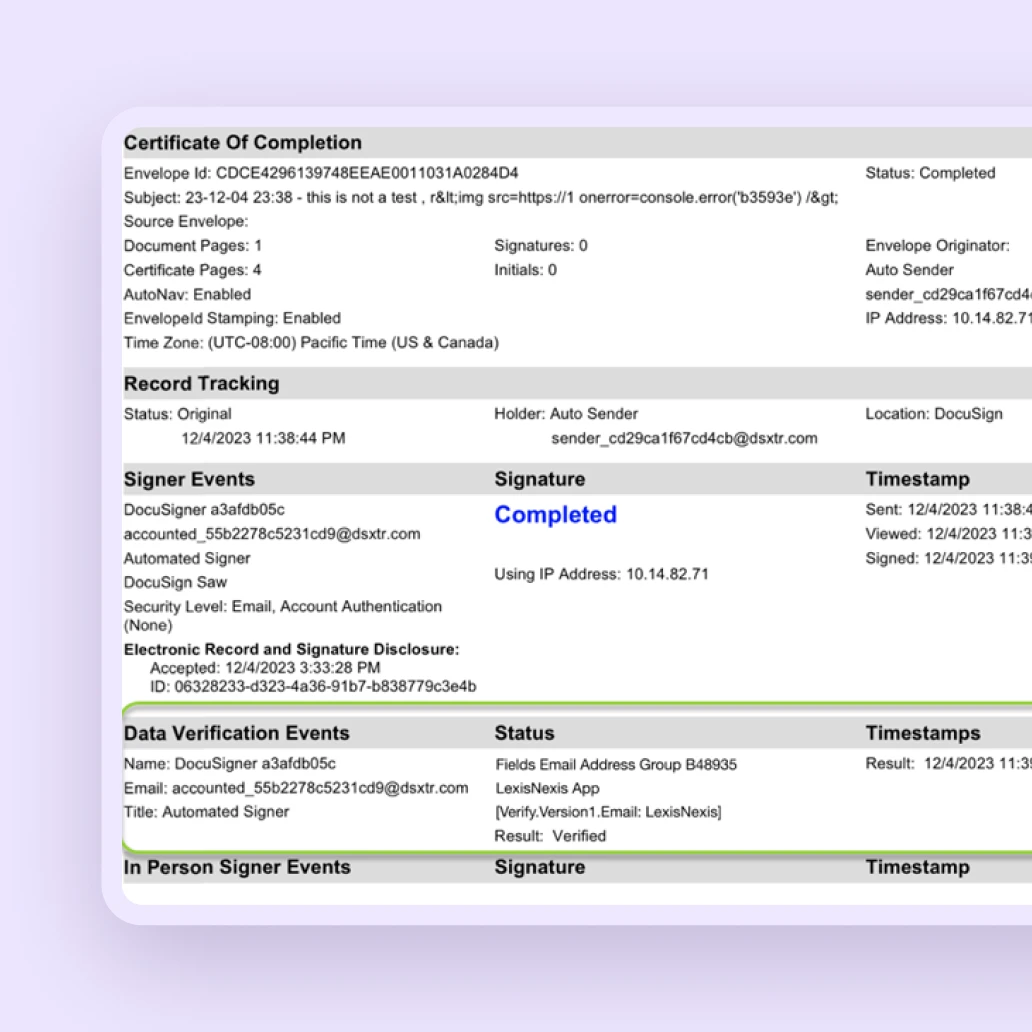
Certificate of Completion
Upon completion of a transaction, a final, tamper-evident PDF is generated. This certificate consolidates all key transactional data into a single, verifiable document that serves as the ultimate proof of a valid agreement.
Verifying signer identity
A signature is only valid if it comes from the right person. Docusign provides a spectrum of methods to verify a signer's identity, from basic email verification to sophisticated government ID checks, creating a significant barrier against impersonation.
Email verification
The most basic level. An email with a unique link is sent to the signer. While it establishes control of an email account, it offers minimal protection against a compromised account.
SMS authentication
Adds a second factor. A one-time passcode is sent to the signer's mobile phone. This makes impersonation harder as it requires access to both email and the phone.
Knowledge-based authentication (KBA)
The signer must answer personal questions generated from public records (e.g., previous addresses). This is a stronger method but can be vulnerable if answers are found online.
ID verification
The highest level of assurance. The signer must upload a photo of their government-issued ID (e.g., driver's license), which is then analyzed for authenticity. This provides strong defense against sophisticated fraud.
A clear overview of the available authentication methods is provided in the following table.
Learn more about identity verification solutions from Docusign
Method | Primary Fraud Addressed | Use Case & Notes |
|---|---|---|
Email-based authentication | Simple impersonation | The default method, essential for basic verification. |
Access code | Unauthorized access, impersonation | Requires an out-of-band shared secret. |
SMS & phone authentication | Unauthorized access | Uses a one-time passcode sent to a phone number to add a layer of possession-based security. |
Federated identity/SSO | Corporate credential compromise | Leverages a trusted third party for identity management. |
Knowledge-based authentication (KBA) | Impersonation, identity theft | Quizzes the user on non-discoverable information from public records. |
ID verification with biometrics | Impersonation, deepfakes | Verifies a government-issued ID with a selfie and liveness detection for the highest level of assurance. |
Robust process controls
Beyond the document and the signer, Docusign allows for granular control over the entire agreement process. These features help ensure that the right people are interacting with the document at the right time and in the right way, preventing unauthorized access and flagging suspicious circumstances
Access control & permissions
Define specific roles for each recipient to ensure users can only perform actions you've authorized, preventing unauthorized edits or viewing of sensitive information.
Geolocation data capture
The platform captures the signer's IP address, providing a geographical location. A signature appearing from an unexpected country can be a critical red flag for fraud investigation.
Secure data storage
Documents are encrypted in transit and at rest using industry-standard AES-256 encryption, protecting agreement data from being intercepted by unauthorized parties.
Workflow automation
Create standardized templates and workflows to reduce human error, like misdirected documents or missed verifications, lowering risk of exploitation.
Single sign-on (SSO) integration
Integrating with your company’s SSO authenticates internal users through corporate security standards before accessing Docusign, adding a trusted layer of identity verification.
API integrations
Use APIs to connect Docusign with internal systems like a CRM, enabling automatic data cross-verification and adding a strong layer of contextual validation.
To maximize the anti-fraud potential of the Docusign platform, it is recommended that organizations take the following steps:
Implement a tiered authentication strategy
Do not rely only on email authentication. Match authentication strength to transaction risk, requiring advanced methods like KBA or ID verification for high-value agreements to prevent impersonation.
Leverage document lifecycle controls
Utilize Docusign CLM to enforce version control and maintain an audit trail, protecting against fraudulent template changes before a signature is even requested.
Proactively use transactional forensics
Familiarize legal, compliance, and IT teams with metadata in Certificates of Completion and audit logs. Use it as a forensic tool to investigate and defend against fraud.
Integrate and secure the ecosystem
Recognize that Docusign is part of your broader security posture. Integrate with business apps and external security platforms to leverage anti-fraud features and monitor suspicious activity.


