Docusign IAM | Standards-Based Signatures
Easy-to-use digital signatures
Solutions that support all levels of digital signatures.


Digital signatures from Docusign
Electronic signatures are widely accepted as part of a modern system of agreement. But some businesses, regions and specific use cases may require digital signatures, which offer a heightened level of identity assurance through digital certificates.
Docusign supports digital signatures to local standards, no matter where you are or what your use case is. Based on our robust eSignature platform, Docusign Standards-Based Signatures offers easy-to-use solutions that support all levels of digital signatures:
• Electronic signatures
• Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES)
• Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES)
Standards-Based Signature benefits
- Offer a cloud-based signing experience
Deliver a simple, easy-to-use signing experience from the cloud. Let signers use the digital signature options integrated with the eSignature interface without downloading plug ins or software.
- Support unique compliance standards
Meet standards for digital signatures, including advanced and qualified levels under EU eIDAS (AES and QES) and industry standards such as 21 CFR Part 11.
- Get started quickly
Digital signature capabilities are embedded into your existing Docusign eSignature and Identify workflows. Use our pre-built integrations or APIs to quickly connect to the systems you already use.
Docusign supports all levels of signature
Combine the power of eSignature and Identify to easily and quickly complete digital signatures.
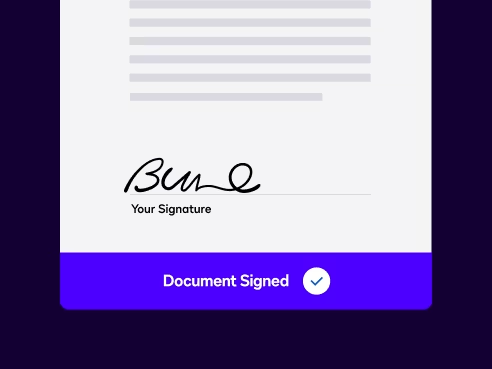 Electronic Signature
Electronic SignatureDocusign eSignature is trusted by hundreds of millions of users world-wide and meets electronic signature regulations, including eIDAs.
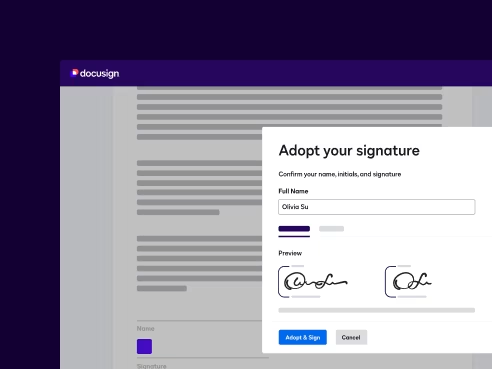 Advanced Electronic Signature
Advanced Electronic SignatureAdd Docusign ID Verification to your electronic signature process to validate signer identity and support AES. This is needed in use cases that require stricter identity assurance.
 Qualified Electronic Signatures
Qualified Electronic SignaturesMeet EU and UK QES standards by combining eSignature with our ID Verification for EU Qualified offering or partner solutions. QES is the only signature legally equivalent to a handwritten signature in the EU, and is preferred for highly regulated use cases or cross-border transactions.

Global Network of Trust Service Provider partners
Docusign integrates with a global network of ID and trust services. Since all digital signatures include a digital certificate issued by a Trust Service Provider, these integrations support your efforts to comply with digital signature standards around the globe from a single cloud-based solution.
One million customers from over 180 countries
Customers use digital signatures for many types of agreements
Account openings
Investment and private banking
Trusts and pensions
Medical records and evidence
Partner and vendor agreements
Insurance agreements
Clinical research portals
HR documents (terminations, temp worker agreements)
Consumer loans
Contracts or inheritance
Manufacturing quality management
Engineer change process/approvals
Resources
Learn more about digital signatures
- Digital Signatures for the EU
Learn more about Docusign solutions for digital signatures.
- New: ID Verification for EU Qualified
Learn how to enhance your security and achieve EU- and UK-compliant QES in minutes with our new ID Verification for EU Qualified offering.
- Implementing Electronic Signatures and Digital Signatures with Docusign
Learn more about the different types of digital signatures and which ones are relevant for your specific use case.
Standards-Based Signature FAQs
Electronic signatures, or e-signatures, are a broad category of methods for signing a document. A digital signature is a type of electronic signature that offers additional verification of the identities of the parties involved in a transaction.
Digital signatures are based on a technology standard called Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). PKI is used to create a unique, tamper-evident “digital certificate” that associates a signer with a document and guarantees that the electronic document is authentic. Digital certificates indicate that the signers have completed extra steps to confirm their identities. A signer’s digital certificate is used to create the signature and then attach it to the signed document.
Advanced electronic signatures (AES) add ID verification to the electronic signature signing process. Signatures must be uniquely linked to, and able to identify, the signer. Signature records are capable of showing evidence of tampering.
Qualified electronic signatures (QES) have more stringent requirements mandating face-to-face, or equivalent, identity verification (the face-to-face identification can be live and in-person or via an audio/video connection.) A QES is unique in that it’s considered legally equivalent to a handwritten signature under eIDAS.In the U.S, digital signatures are typically used in regulated industries like life sciences for compliance with the FDA’s requirements for electronic signatures, often referred to as 21 CFR Part 11. Another example is the US Federal Government, where federal employees can be issued a personal identity verification (PIV) card that contains a PKI digital certificate for signing that complies with the US Federal Processing Standards.
Around the world, there are international standards that specify requirements for digital signatures and the methods used to authenticate a signer. Regulations include the Electronic Identification, Authentication and Trust Services regulation (eIDAS) in the EU, the Electronic Transactions Acts in Australia, Code of Civil Procedure in Brazil and Section 1803 of the Civil Code in Mexico,
Docusign works with Trust Service providers from around the world to offer digital certificates and digital signatures through the Docusign platform.
Digital signatures are available worldwide with Docusign Standards-Based Signatures
